Free ASVAB Practice Tests
-
Every Test is UniqueCustom software and unique templates randomize questions, answers, and variables every time you take a new test. You'll never take the same test twice!
-
1,557 Questions, Problems & Flash CardsHuge database of 668 multiple-choice questions, 135 math and algebra problems, and 754 flash cards to help you prepare for the ASVAB.
-
Detailed SolutionsGet a question wrong? All questions and problems have detailed answer explanations so you can learn exactly how to get it right the next time.
-
Know You're ReadyWant to know how you stack up? When you're done with a practice test you can compare your score to everyone else who has ever answered those questions.
-
Interactive Study GuideDetailed ASVAB study guide, MOS study guides, and line score study guides outline exactly what you should know to earn your target scores and customized tests and flash cards for each topic let you laser focus your limited study time.
-
Brand New for 2019ASVAB Test Bank has been completely redesigned for 2019 with all new questions, problems, and flash cards. And the redesign isn't done! Coming soon:
- More Content
- More questions, problems and flash cards
- Bookmarks
- Create a custom study guide with just the topics you're studying
- Score Estimator
- Custom estimate of your potential ASVAB score
Plus printable tests, Q&A, and an ad-free upgrade. Have a suggestion? Please let us know what you want!
Take an ASVAB Practice Test
Sample Practice Test Questions

This tool is a(n) __________.
chisel
A chisel has a long sharp edge and is used, often in conjunction with a hammer, for cutting. In woodworking, chisels are used to remove large sections of wood to create the initial shape of a design. In metalworking, chisels are used to remove waste metal when a smooth finish is not required.
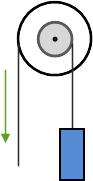 The radius of the axle is 3, the radius of the wheel is 4, and the blue box weighs 35 lbs. What is the effort force necessary to balance the load?
The radius of the axle is 3, the radius of the wheel is 4, and the blue box weighs 35 lbs. What is the effort force necessary to balance the load?
The mechanical advantage of a wheel and axle is the input radius divided by the output radius:
MA = \( \frac{r_i}{r_o} \)
In this case, the input radius (where the effort force is being applied) is 4 and the output radius (where the resistance is being applied) is 3 for a mechanical advantage of \( \frac{4}{3} \) = 1.33
MA = \( \frac{load}{effort} \) so effort = \( \frac{load}{MA} \) = \( \frac{35 lbs.}{1.33} \) = 26.32 lbs.
Which of the following is not a characteristic of direct current?
an example power source is a generator
Direct current flows in only one direction in a circuit, from the negative terminal of the voltage source to the positive. A common source of DC is a battery. In contrast to the constant one-way flow of direct current, alternating current changes direction many times each second. Electricity is delivered from power stations to customers as AC because it provides a more efficient way to transport electricity over long distances.
__________ and __________ pair to strengthen bones.
vitamin D, calcium
Vitamin D helps calcium strengthen bones while also aiding muscle, nerve, and immune system function.
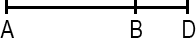
If BD = 22 and AD = 29, AB = ?
The entire length of this line is represented by AD which is AB + BD:
AD = AB + BD
Solving for AB:AB = AD - BDAB = 29 - 22
AB = 7
What is the potential difference in an electrical circuit a measure of?
the voltage at a specific location in the circuit
Electrons flow from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. A high voltage indicates a high concentration of electrons that creates a greater potential for electron flow than a low voltage. When applied to a load, voltage creates electricity and potential difference is the measure of voltage at a specific location in an electrical circuit.
Which of the following is the narrowest classification of life?
species
The narrowest classification of life, species, contains organisms that are so similar that they can only reproduce with others of the same species.
You're replacing the hubcaps on a car. Which of the following are you most likely to use?
rubber mallet
A mallet is a hammer with a relatively large head, often made of rubber or wood. Both the size and material of the mallet head help prevent damage when striking more delicate surfaces.