Free ASVAB Practice Tests
-
Every Test is UniqueCustom software and unique templates randomize questions, answers, and variables every time you take a new test. You'll never take the same test twice!
-
1,557 Questions, Problems & Flash CardsHuge database of 668 multiple-choice questions, 135 math and algebra problems, and 754 flash cards to help you prepare for the ASVAB.
-
Detailed SolutionsGet a question wrong? All questions and problems have detailed answer explanations so you can learn exactly how to get it right the next time.
-
Know You're ReadyWant to know how you stack up? When you're done with a practice test you can compare your score to everyone else who has ever answered those questions.
-
Interactive Study GuideDetailed ASVAB study guide, MOS study guides, and line score study guides outline exactly what you should know to earn your target scores and customized tests and flash cards for each topic let you laser focus your limited study time.
-
Brand New for 2019ASVAB Test Bank has been completely redesigned for 2019 with all new questions, problems, and flash cards. And the redesign isn't done! Coming soon:
- More Content
- More questions, problems and flash cards
- Bookmarks
- Create a custom study guide with just the topics you're studying
- Score Estimator
- Custom estimate of your potential ASVAB score
Plus printable tests, Q&A, and an ad-free upgrade. Have a suggestion? Please let us know what you want!
Take an ASVAB Practice Test
Sample Practice Test Questions
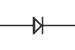
This circuit component symbol represents a(n):
diode
A diode allows current to pass easily in one direction and blocks current in the other direction. Diodes are commonly used for rectification which is the conversion of alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). Because a diode only allows current flow in one direction, it will pass either the upper or lower half of AC waves (half-wave rectification) creating pulsating DC. Multiple diodes can be connected together to utilize both halves of the AC signal in full-wave rectification.
Menstruation occurs when:
the ovum fails to become fertilized
If the ovum fails to become fertilized, the lining of the uterus sloughs off during menstruation. From puberty to menopause, this cycle of menstruation repeats monthly (except during pregnancy).
The most diverse kindgom of life is which of the following?
protists
Below domain, life is classified into six kingdoms: plants, animals, archaebacteria, eubacteria, and fungi. The last kingdom, protists, include all microscopic organisms that are not bacteria, animals, plants or fungi. (Archaebacteria and eubacteria are sometimes combined into a single kingdom, monera.)
When two lines intersect, adjacent angles are __________ (they add up to 180°) and angles across from either other are __________ (they're equal).
supplementary, vertical
Angles around a line add up to 180°. Angles around a point add up to 360°. When two lines intersect, adjacent angles are supplementary (they add up to 180°) and angles across from either other are vertical (they're equal).
The joule is a unit of measurement for:
energy
The joule is a unit of measurement for energy.
A right angle measures:
90°
A right angle measures 90 degrees and is the intersection of two perpendicular lines. In diagrams, a right angle is indicated by a small box completing a square with the perpendicular lines.
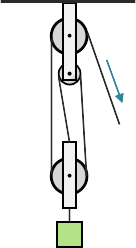
Which of the following statements about this pulley configuration is false?
Only multiplies the effort force
A block and tackle is a combination of one or more fixed pulleys and one or more movable pulleys where the fixed pulleys change the direction of the effort force and the movable pulleys multiply it. The mechanical advantage is equal to the number of times the effort force changes direction and can be increased by adding more pulley wheels to the system. An easy way to find the mechanical advantage of a block and tackle pulley system is to count the number of ropes that support the resistance.
According to Boyle's law, for a fixed amount of gas kept at a fixed temperature, which of the following are inversely proportional?
pressure, volume
Boyle's law states that "for a fixed amount of an ideal gas kept at a fixed temperature, pressure and volume are inversely proportional".